Understanding the different types of diabetes can be one of the first steps to tackling the disease. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Prediabetes indicates a higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes and its complications, and it can also lead to type 2 diabetes if left untreated. This type of diabetes is caused by having high blood sugar levels because you don’t produce enough insulin or your body doesn’t respond properly to insulin.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
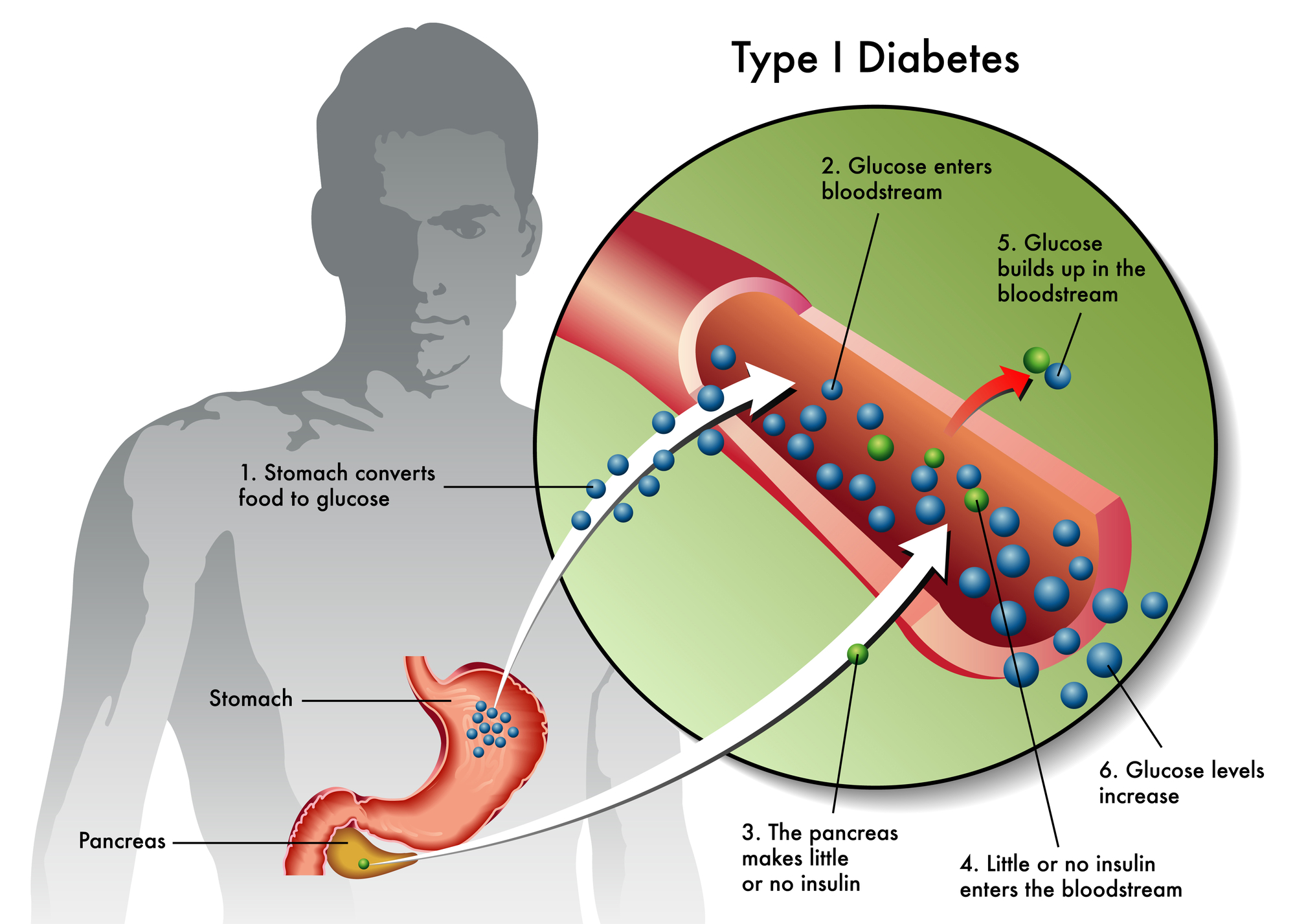
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to control blood sugar levels.
People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day to stay alive. Without insulin, the body’s cells cannot get the glucose they need for energy.
Type 1 diabetes can develop at any age, but it most often occurs in children and young adults. It is also known as juvenile diabetes or early-onset diabetes.
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes can develop suddenly and may include:
– increased thirst
– frequent urination
– extreme hunger
– weight loss
– fatigue
– blurred vision
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor right away. With early diagnosis and treatment, people with type 1 diabetes can live long and healthy lives.
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the beta cells in the pancreas.
The beta cells are responsible for producing insulin, which is a hormone that helps to regulate blood sugar levels. When the beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
There is no known cure for type 1 diabetes, but it can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes.
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
How to Prevent Type 1 Diabetes
Diabetes Care & Management
Conclusion


Recent Comments